Supported Source and Destination Database Types
The following table describes the supported source and destination database types.
| Source Database Types | Destination Database Types |
|---|---|
| RDS MySQL and self-managed MySQL 5.6/5.7/8.0 | RDS FOR MYSQL |
Note: The engine of a self-managed MySQL database can be MySQL 5.6, 5.7, or 8.0, and the engine version of the destination database must be equal to or later than that of the source database.
Supported Migration Objects and SQL Operations
DTS supports table-level (specified table objects) migration and database-level (entire database) migration.
DTS supports structure migration of tables, indexes, stored procedures, views, functions, events, and triggers.
The names of tables that store data of views, stored procedures, and functions cannot be mapped to new names in the destination database.
During structure migration, DTS changes the definers of the views, functions, stored procedures, triggers, and events to the account that is used to access the destination database. Then, the original definers have only the invoker permissions on these objects.
DTS only migrates user databases and automatically filters out system databases. For example, DTS does not migrate information_schema, mysql, performance_schema, and sys databases in MySQL.
DTS migrates triggers and events after the full data migration is complete.
An empty database without tables, views, functions, events, triggers, or stored procedures cannot be used as a source database.
SQL Operations Supported During Incremental Data Migration
DML
INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE
DDL
For incremental data migration, only the following DDL statements are supported: CREATE INDEX, DROP INDEX, ALTER TABLE, TRUNCATE TABLE, and DROP TABLE. For database-level migration, CREATE TABLE is supported.
Note: DTS does not support the following statement: CREATE TABLE Table name AS SELECT.
Database Accounts and Permissions
The following table describes the information about database accounts and required permissions.
| Database | Required Permissions | Sample Statement for Granting Permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Source Database | 1. Query permissions on MySQL databases. 2. Query permissions on the databases to be migrated. 3. Certain global permissions: RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE, SHOW VIEW, and PROCESS. 4. To migrate an entire instance, the query permissions on all databases in the source instance are required. | GRANT SELECT ON mysql. TO 'Account used for migration'@'%'; GRANT SELECT ON Source database. TO 'Account used for migration'@'%'; GRANT RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE, SHOW VIEW, PROCESS ON . TO 'Account used for migration'@'%'; |
| Destination Database | The following 23 global permissions are required: ALTER ALTER ROUTINE CREATE CREATE ROUTINE CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES CREATE USER CREATE VIEW DELETE DROP EVENT EXECUTE INDEX INSERT LOCK TABLES PROCESS REFERENCES RELOAD SELECT SHOW DATABASES SHOW VIEW TRIGGER UPDATE | GRANT ALTER, ALTER ROUTINE, CREATE, CREATE ROUTINE, CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES, CREATE USER, CREATE VIEW, DELETE, DROP, EVENT, EXECUTE, INDEX, INSERT, LOCK TABLES, PROCESS, REFERENCES, RELOAD, SELECT, SHOW DATABASES, SHOW VIEW, TRIGGER, UPDATE ON*.*TO 'Account used for migration'@'%'; |
Precautions
If you want to migrate some tables in a database, you can select up to 600 tables in a single data migration task. If you select more than 600 tables, a request error is returned after you submit the task. In such a case, we recommend that you configure multiple tasks to migrate the tables, or configure a task to migrate the entire database.
We recommend that you enable global transaction identifier (GTID) for the source database. If GTID is disabled for the source database, DTS does not support primary-standby switchover for high availability because DTS tasks will be interrupted during primary-standby switchover and cannot be restored due to offset discontinuity.
The character set of the destination RDS database must be the same as that of the source database.
Make sure that the destination database is empty before starting a migration task. If the destination database contains data rows, we recommend that you clear the existing data. If the destination database and the source database contain data with the same primary key values, the existing data in the destination database will be overwritten during DTS incremental data migration.
The binlog feature must be enabled for the source MySQL database, and the row-based format is used for binary logging.
If the storage space is sufficient, store the source database binlogs as long as possible. The recommended retention period is seven days. If the binlog retention period is too short, DTS may fail to obtain the required binlogs during incremental data migration and fails to migrate incremental data. Make sure that you configure a binlog retention period in accordance with the migration requirements. The DTS Service Level Agreement (SLA) is not applicable to issues caused by an insufficient binlog retention period.
The destination database and the RDS instance to which the destination database belongs must be running normally. If the RDS instance uses the primary/standby architecture, the primary/standby replication must run as expected.
The destination RDS database instance must have sufficient storage space. During full data migration, concurrent INSERT operations cause table fragmentation in the destination database. Therefore, the size of the used tablespace in the destination database is larger than that in the source database instance. In addition, a large number of binlogs generated during migration also require a large storage space.
If the destination database instance uses a column of the TIMESTAMP or DATETIME data type as the shard key, the seconds hierarchy in the column is removed after migration.
DTS does not migrate user information. If a user needs to call views, stored procedures, or functions in the destination database after migration, you must grant the read and write permissions on the objects to the user.
You are not recommended to perform DDL operations to delete data from the source database during task startup or full data migration. Otherwise, the migration may fail.
During migration, do not modify or delete the usernames, passwords, permissions, or ports of the source and destination databases.
During migration, do not modify the table structures to be migrated in the source database.
If you migrate selected tables, you are not recommended to rename the tables during incremental data migration.
During incremental data migration, the source database cannot be restored.
During incremental data migration, DTS does not migrate incremental data added to the source tables without primary keys. DTS provides lower migration performance for tables without primary keys than those with primary keys. In addition, DTS cannot ensure data consistency if incremental data is added to the source tables without primary keys during migration.
Procedure
After a DTS instance is created, it is in the To be configured status. Click Configuration.
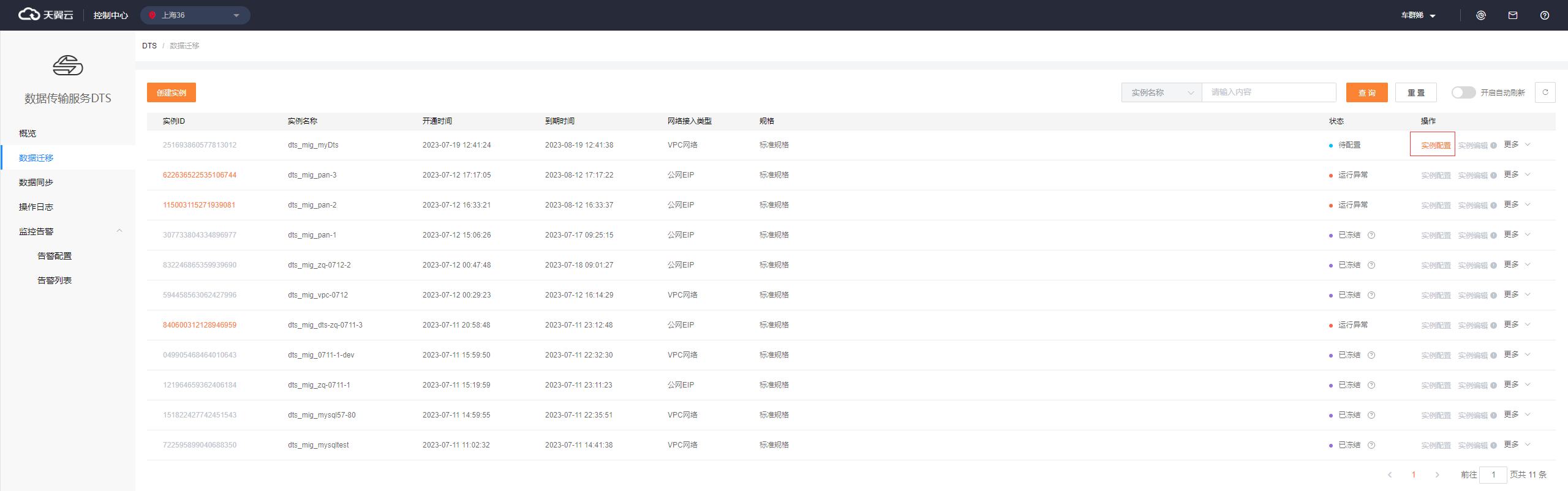
Configure Source and Destination Databases
Configure information about the source and destination databases, including the database types, IP addresses, ports, database accounts, and passwords.
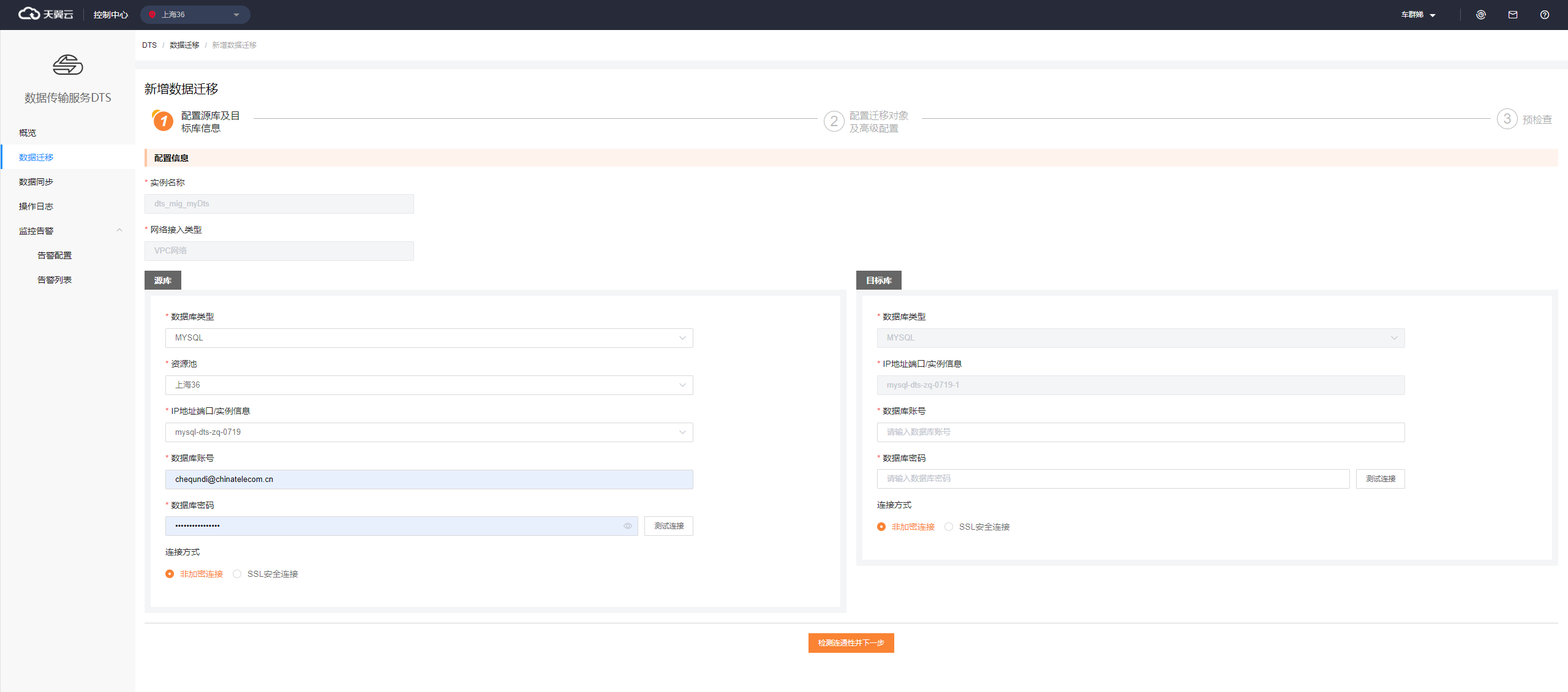
After you enter all required information about the source and destination databases, you can perform a connectivity test to check whether the databases can be connected.After you configure the source and destination databases, click Test Connectivity and Proceed. On the Configure Objects and Advanced Settings page that appears, select the objects that you want to migrate.
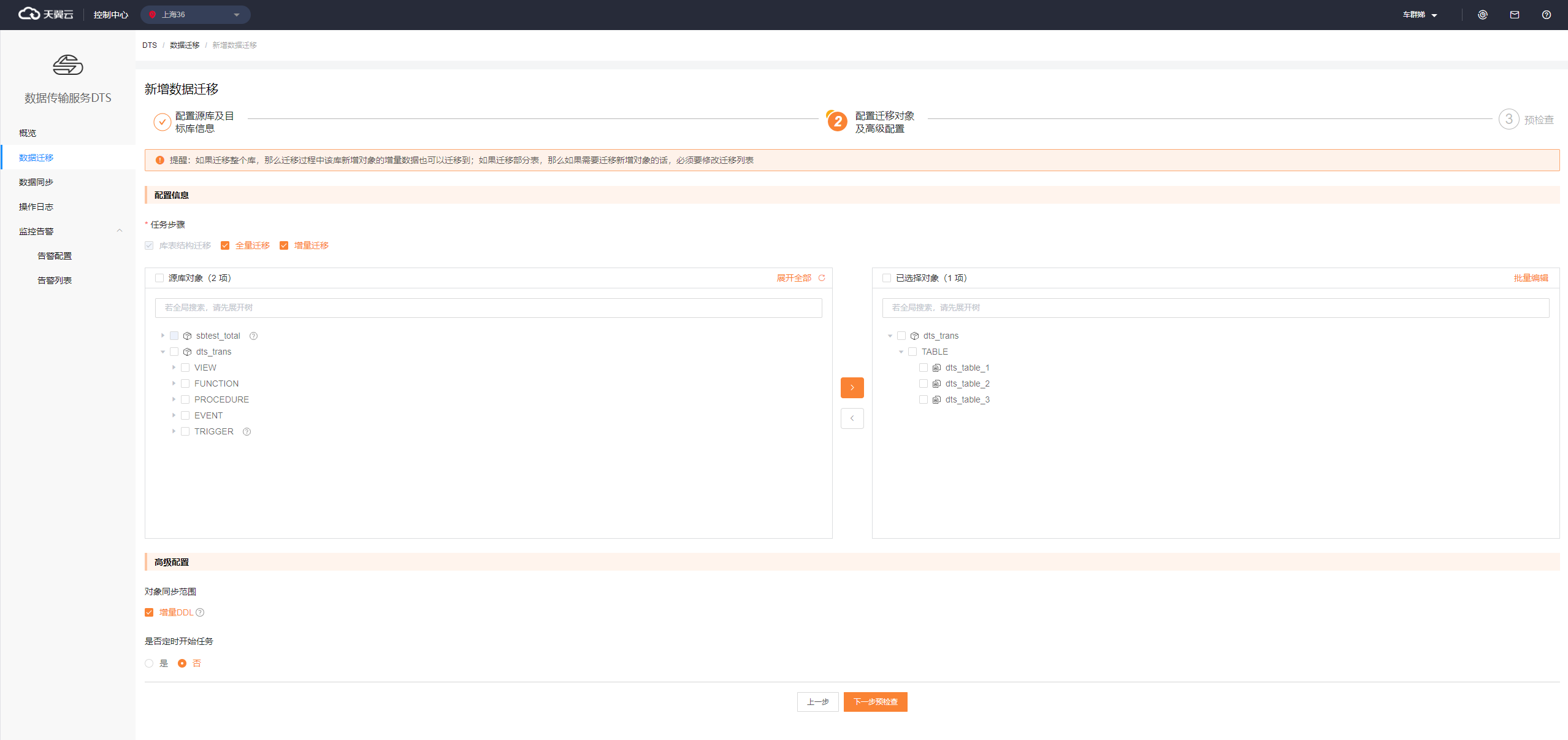
Note: For more information about how to configure objects and advanced settings, see Configuring and Editing an Instance > Configuring a Migration Instance.Click Next: Precheck. The system checks the items listed on the Precheck page and provides check results. You can perform subsequent operations based on the check results.
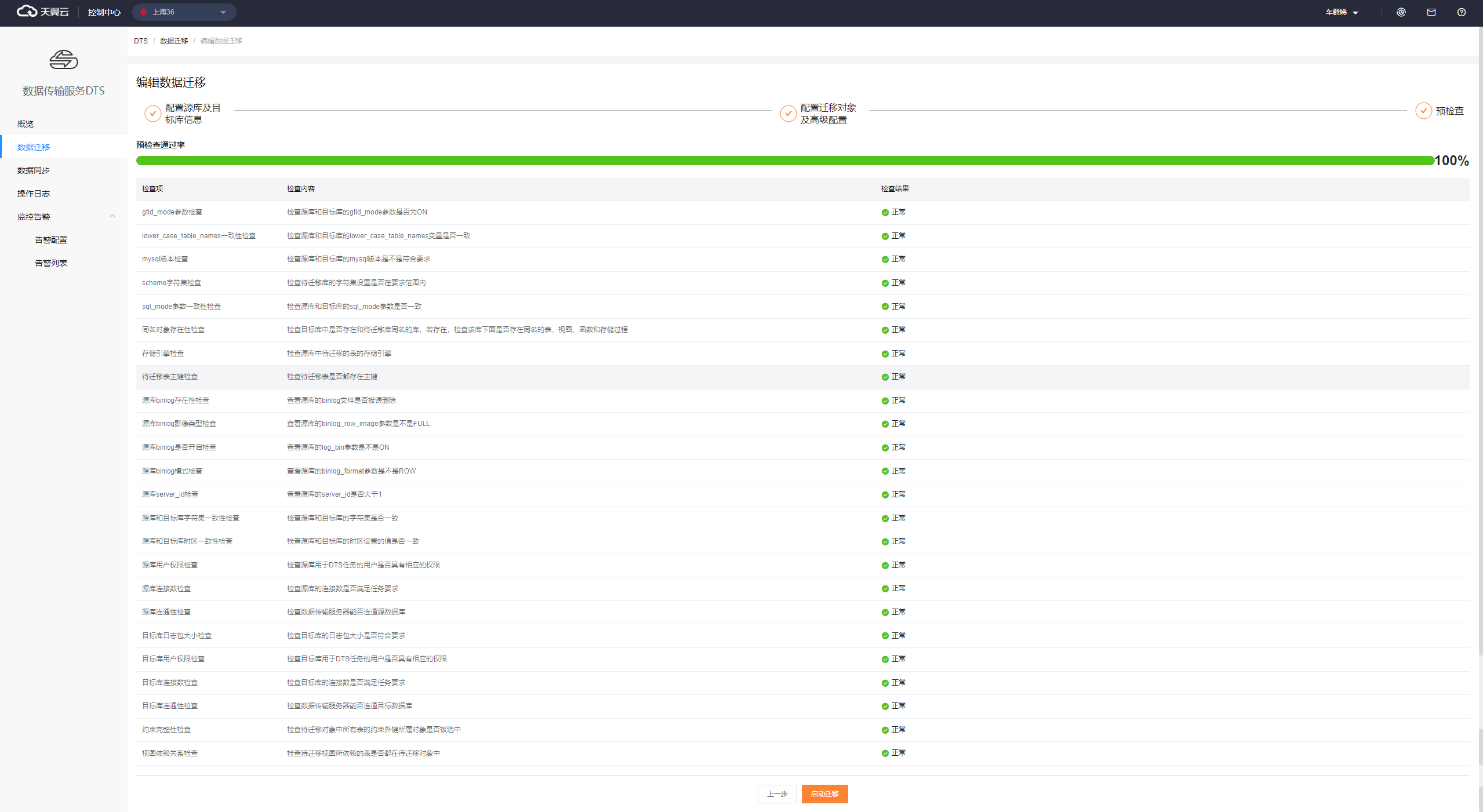
If the precheck is passed, click Start Migration to start the data migration task.

